Longevity and High Power Cycling Capability
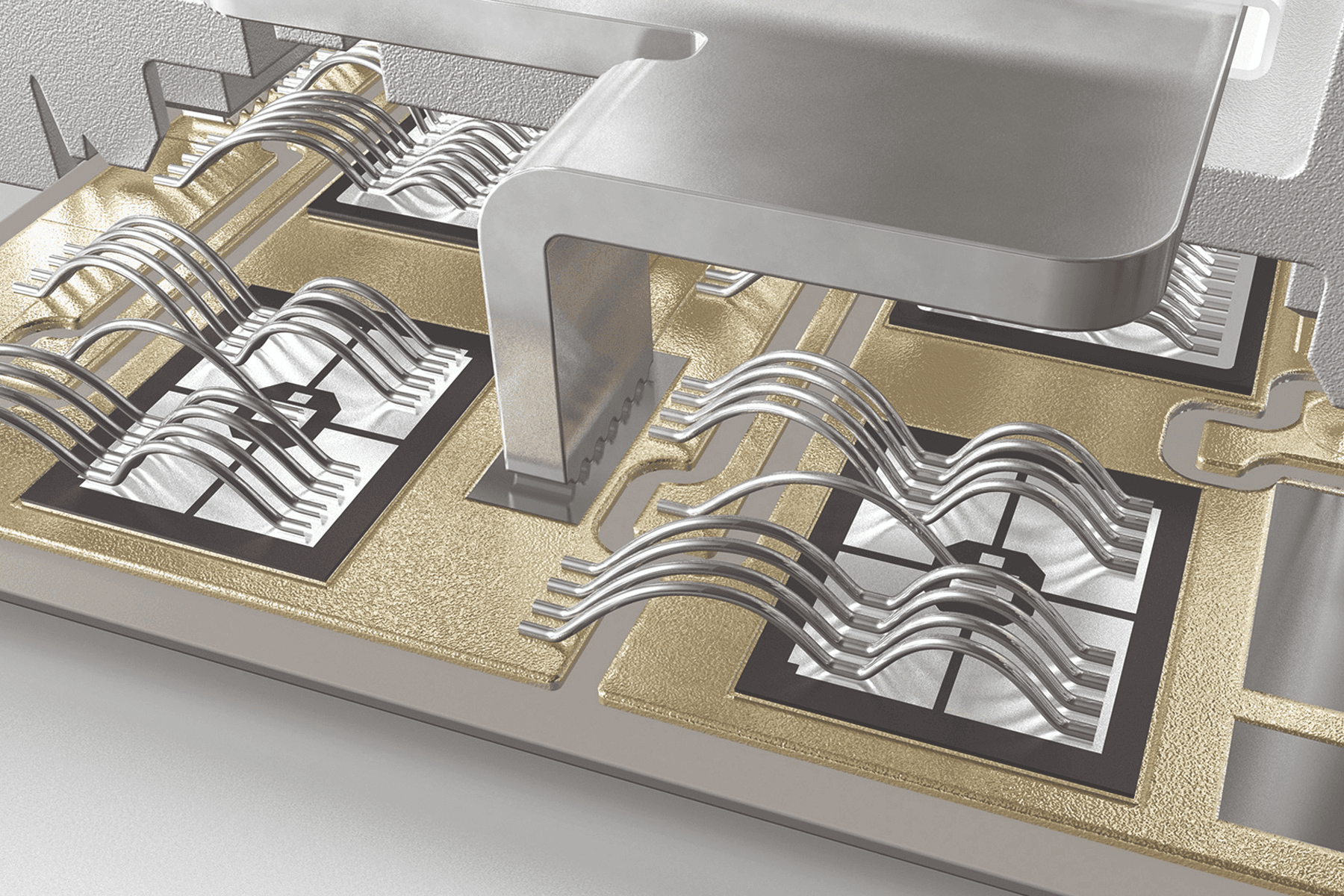
First developed in 1992, SKiiP Technology utilizes a baseplate-less direct bonded copper (DBC) substrate that is pressed onto a heatsink in multiple places using a specially designed pressure element. This same element can also apply high pressure to busbar or spring terminals to make electrical contact between the DBC substrate and outside circuits. The use of a pressure frame allows for mounting pressure to be evenly distributed across the DBC substrate — close to chips — providing excellent thermal contact to the underlying heatsink.
SKiiP Technology can be implemented with any type of heatsink and a variety of power modules employing this technology are available. The SKiiP IPM is available with a variety of air- or water-cooled types. The MiniSKiiP module implements SKiiP Technology in a standalone module that the user can mount as needed.
